SAN,SCSI等介绍
最近在使用ceph的iSCSI driver时,发现一些存储相关的术语让人很困惑,也不清楚背后的技术。这篇文章记录了一些调研结果。
术语
以下是摘自wikipedia的,很多存储相关术语的解释,在试图搞清楚这些技术所处的层次,和之间的关系前,先让我们弄清楚他们的定义。
-
SAN:A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to enhance accessibility of storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries, to servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as locally-attached devices.
SAN是指存储区域网络,它可以提供统一的,块级别的存储。SAN主要用来增强一些存储设备对server的可用性,使这些设备在操作系统看来,就像是本地连接的设备一样。
-
SCSI: Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, /ˈskʌzi/ SKUZ-ee)[1] is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. SCSI is most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices.
SCSI是定义了计算机和一些外设之间如何互连和传输数据的一系列标准。SCSI标准集定义了命令,协议,电子、光学、以及逻辑接口。SCSI最主要用在硬盘和磁盘,但它也可以连接很多其他设备,比如CD,扫描仪等。
-
ISCSI: In computing, iSCSI (/ˈaɪskʌzi/ (
 listen) EYE-skuz-ee) is an acronym for Internet Small Computer Systems Interface, an Internet Protocol (IP)-based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. It provides block-level access to storage devices by carrying SCSI commands over a TCP/IP network. iSCSI is used to facilitate data transfers over intranets and to manage storage over long distances. It can be used to transmit data over local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), or the Internet and can enable location-independent data storage and retrieval.
listen) EYE-skuz-ee) is an acronym for Internet Small Computer Systems Interface, an Internet Protocol (IP)-based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. It provides block-level access to storage devices by carrying SCSI commands over a TCP/IP network. iSCSI is used to facilitate data transfers over intranets and to manage storage over long distances. It can be used to transmit data over local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), or the Internet and can enable location-independent data storage and retrieval.ISCSI是个基于IP协议的,定义了如何连接存储设备的网络标准,通过在TCP/IP网络上传输SCSI命令,它提供了块级别的存储。它被用来简化数据在内网的传输,和远距离的存储。它也可以被用来通过LAN、WAN,或者Internet来传输数据,同时构造了一种位置无关的数据存取系统。
-
FC: Fibre Channel (FC) is a high-speed data transfer protocol (commonly running at 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, and 128 gigabit per second rates) providing in-order, lossless[1] delivery of raw block data[2], primarily used to connect computer data storage to servers.[3][4] Fibre Channel is mainly used in storage area networks (SAN) in commercial data centers. Fibre Channel networks form a switched fabric because they operate in unison as one big switch. Fibre Channel typically runs on optical fiber cables within and between data centers, but can also run on copper cabling.[3][4]
FC是一种高速的数据传输协议,可提供有序的,无数据丢失的原生的块数据的分发,主要被用来连接存储设备和服务器。它主要备用在商业数据中心的SAN中。Fibre Channel网络向一个大的switch一样协同运作,形成了一个交换组(fabric:结构,组织)。FC通常运行在数据中心内部或数据中心之间的光纤网络上,但也可以运行在銅轴电缆网络之上。
-
FCP: Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) is a transport protocol that predominantly transports SCSI commands over Fibre Channel networks.
FCP是一个主要用在通过FC网络传输SCSI命令的协议。
-
FCoE: Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is a computer network technology that encapsulates Fibre Channel frames over Ethernet networks. This allows Fibre Channel to use 10 Gigabit Ethernet networks (or higher speeds) while preserving the Fibre Channel protocol.
FCoE是一种封装了Fibre Channel帧,在以太网上传输的网络技术。通过这种技术可以允许FC协议运行在10GB或更高速的以太网络之上。
-
FCIP: Fibre Channel over IP (FCIP or FC/IP, also known as Fibre Channel tunneling or storage tunneling) is an Internet Protocol (IP) created by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) for storage technology.An FCIP entity functions to encapsulate Fibre Channel frames and forward them over an IP network. FCIP entities are peers that communicate using TCP/IP. FCIP technology overcomes the distance limitations of native Fibre Channel, enabling geographically distributed storage area networks to be connected using existing IP infrastructure, while keeping fabric services intact. The Fibre Channel Fabric and its devices remain unaware of the presence of the IP Network.
FCIP和FCoE有点相似,但它是将FC帧封装后走了IP网络,所以FCIP可以克服原生的FC协议的距离限制。
-
NFS: Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol originally developed by Sun Microsystems (Sun) in 1984,[1] allowing a user on a client computer to access files over a computer network much like local storage is accessed. NFS, like many other protocols, builds on the Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call (ONC RPC) system.
NFS是一个最初由Sun开发的分布式的文件系统协议,允许用户使用客户端,像访问本地存储一样,通过网络来访问文件。
-
CIFS: In computer networking, Server Message Block (SMB), one version of which was also known as Common Internet File System (CIFS /sɪfs/),[1][2] is a network communication protocol[3] for providing shared access to files, printers, and serial ports between nodes on a network.
CIFS是一个定义了网络中的节点如何共享文件、打印机、串口设备的网络通信协议。
-
DAS: Direct-attached storage (DAS) is digital storage directly attached to the computer accessing it, as opposed to storage accessed over a computer network (i.e. network-attached storage). Examples of DAS include hard drives, solid-state drives, optical disc drives, and storage on external drives. The name “DAS” is a retronym to contrast with storage area network (SAN) and network-attached storage (NAS).
DAS是一个用来和NAS、SAN进行区分的术语,它主要指的是硬盘,固态硬盘,光驱等直连设备。
-
NAS: Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level (as opposed to block-level) computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. NAS is specialized for serving files either by its hardware, software, or configuration. It is often manufactured as a computer appliance – a purpose-built specialized computer.[nb 1] NAS systems are networked appliances which contain one or more storage drives, often arranged into logical, redundant storage containers or RAID.
NAS是一个文件级别的存储服务器,对异构的client提供数据访问服务。NAS不论是从硬件、软件和配置上,都是专门用来服务文件的。
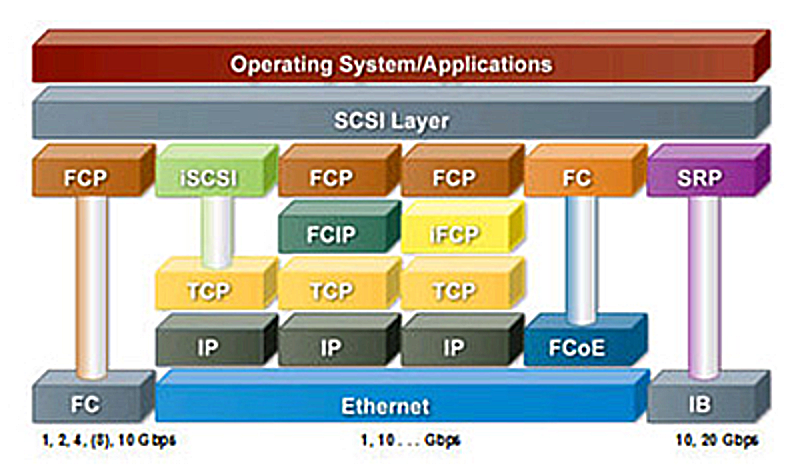
操作系统的视角
这张图从操作系统的视角来描绘了上面提到的很多协议,结合它们的定义,他们的层级关系和互相之间的关联关系便一目了然了。
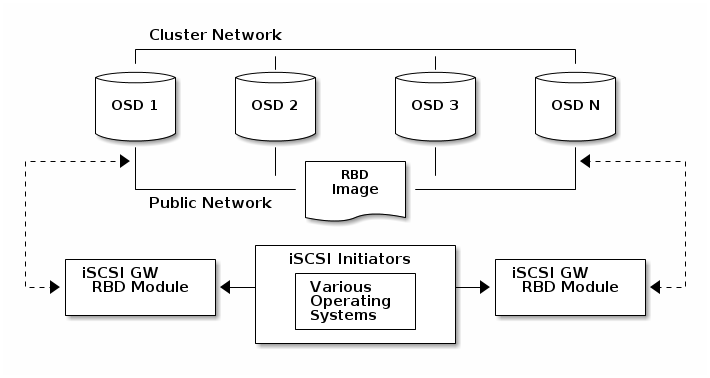
Ceph的SAN实现
ceph实现了iSCSI协议,结合RBD,对外提供块级别存储服务。以下是ceph iSCSI的架构图。